Information technology —
Environmental Data Coding Specification (EDCS)
This International Standard provides mechanisms to specify unambiguously objects used
to model environmental concepts. To accomplish this, a collection of nine EDCS dictionaries
of environmental concepts are specified:
- classifications: specify the type of environmental objects;
- attributes: specify the state of environmental objects;
- attribute value characteristics: specify information concerning the
values of attributes;
- attribute enumerants: specify the
allowable values for the state of an enumerated attribute;
- units: specify quantitative measures of the state of some environmental objects;
- unit scales: allow a wide range of numerical values to be stated;
- unit equivalence classes: specify sets of units that are mutually comparable;
- organizational schemas: useful for locating classifications and attributes sharing a common
context; and
- groups: into which concepts sharing a common context are collected.
A functional interface is also specified.
As denoting and encoding a concept requires a standard way of identifying the
concept, this International Standard specifies labels and codes in the dictionaries.
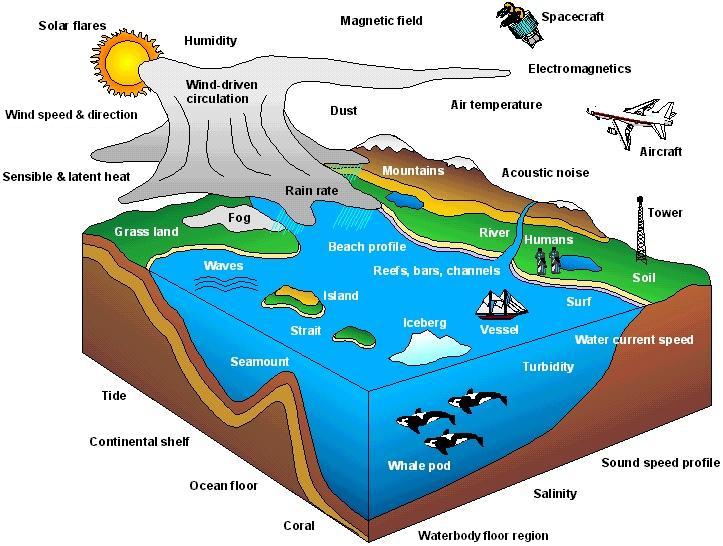
This International Standard specifies environmental phenomena in categories that include, but are not limited to, the
following:
- abstract concepts (e.g., absolute latitude accuracy, geodetic azimuth);
- airborne particulates and aerosols (e.g., cloud, dust, fog, snow);
- animals (e.g., civilian, fish, human, whale pod);
- atmosphere and atmospheric conditions (e.g., air temperature,
humidity, rain rate, sensible and latent heat, wind speed and direction);
- bathymetric physiography (e.g., bar, channel, continental shelf, guyot, reef,
seamount, waterbody floor region);
- electromagnetic and acoustic phenomena (e.g., acoustic noise, frequency, polarization,
sound speed profile, surface reflectivity);
- equipment (e.g., aircraft, spacecraft, tent, train, vessel);
- extraterrestrial phenomena (e.g., asteroid, comet, planet);
- hydrology (e.g., lake, rapids, river, swamp);
- ice (e.g., iceberg, ice field, ice peak, ice shelf, glacier);
- man-made structures and their interiors (e.g., bridge, building, hallway, road, room,
tower);
- ocean and littoral surface phenomena (e.g., beach profile, current, surf, tide, wave);
- ocean floor (e.g., coral, rock, sand);
- oceanographic conditions (e.g., luminescence, salinity, specific gravity,
turbidity, water current speed);
- physiography (e.g., cliff, gorge, island, mountain, reef, strait, valley region);
- space (e.g., charged particle species, ionospheric scintillation, magnetic field, particle
density, solar flares);
- surface materials (e.g., concrete, metal, paint, soil); and
- vegetation (e.g., crop land, forest, grass land, kelp bed, tree).
Figure 1.1 illustrates some of these environmental phenomena.
http://standards.iso.org/ittf/PubliclyAvailableStandards/index.html