This clause specifies concepts behind the abstract structure that all encoded transmittals shall follow and that all encodings shall support.
References are made to Part 1 of ISO/IEC 18023 throughout this part of ISO/IEC 18023. Such references are italicized to set them apart from the surrounding text.
Table 4.1 lists the topics for this clause.
The SEDRIS abstract transmittal format provides a platform independent interchange mechanism for SEDRIS transmittals. The abstract transmittal format is a conceptual file format that defines the organization of a persistent SEDRIS transmittal as specified in 5 Transmittal structure.
A SEDRIS transmittal is composed of one or more files. When a SEDRIS transmittal is comprised of more than one file, one of the files is the root file and all of the other files are object files as specified in 5 Transmittal structure. The root file is the one that is initially accessed when a SEDRIS transmittal is opened.
The abstract transmittal format specifies an abstract structure that shall be followed by actual transmittal format encodings including that specified in Part 3 of ISO/IEC 18023. Other encodings are allowed and would provide representations for their own purposes that are compliant with the abstract transmittal format (see 6.3 Conformance of encodings).
The abstract transmittal format specifies a conceptual representation of a SEDRIS transmittal for storage in a persistent form. The objects may be conceptually stored throughout one or more files. The exact representation of the SEDRIS transmittal is determined by the particular encoding. The abstract transmittal format specifies the allowable structure that shall be satisfied by an encoded SEDRIS transmittal as detailed in 5 Transmittal structure.
In addition to the data embodied by objects, the abstract transmittal format provides for the inclusion of format specific additional data necessary to organize the objects according to the dictates of each particular encoding. The additional information is represented in the abstract syntax as “encoding elements”. Encoding elements may include such items as file and block headers for a binary encoding or end-of-line elements for a clear text encoding. The locations at which such items may appear are specified in the abstract syntax.
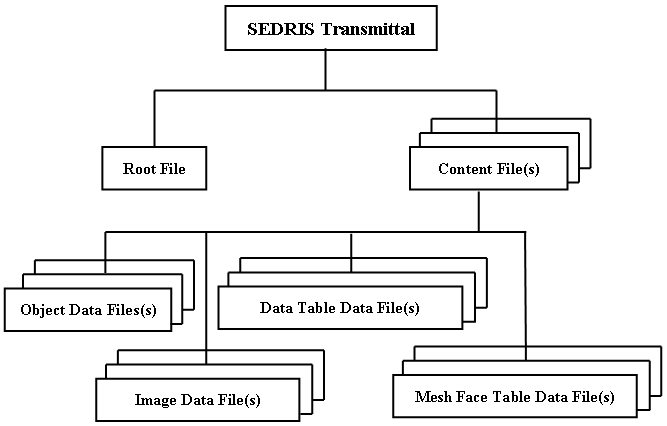
Figure 4.1 depicts the abstract form of an encoded SEDRIS transmittal. The specific encoding shall specify the actual realized organization of data allowed within that encoding. A SEDRIS transmittal may be expressed as one or more files depending on the characteristics of the specific encoding.
Figure 4.1 — Abstract encoded transmittal layout
An encoding may support compression for individual elements within the encoding, groups of elements within the encoding, and/or the entire transmittal. If an encoding allows compression, only loss-less compression techniques shall be used.
http://standards.iso.org/ittf/PubliclyAvailableStandards/ISO_IEC_18023-2_Ed1.html